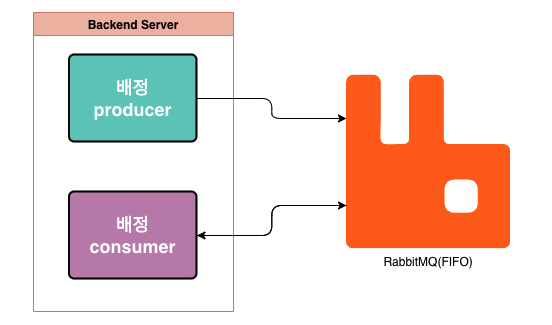
Memphis is an open-source message queuing and streaming platform that has gained a lot of traction in recent years due to its powerful features and ease of use. It was created to solve the problems of scaling, reliability, and performance in large-scale distributed systems. In this article, i will take a deep dive into Memphis and compare it with RabbitMQ and Kafka, which are similar technology stacks. I will also show you an example of how to use Memphis in detail and discuss the limitations that still exist.
Overview of Memphis
Memphis is a highly performant messaging system that is designed to be easy to use and highly scalable. It is built on top of the Rust programming language and leverages the power of modern hardware to deliver exceptional performance. Memphis is designed to be highly fault-tolerant and can handle the loss of nodes in a cluster without any loss of data or service interruption. It uses a peer-to-peer architecture that allows for seamless horizontal scaling.
Characteristics of Memphis
 One of the biggest strengths of Memphis is its ease of use. It comes with a simple and intuitive API that makes it easy to get started with. It also has an excellent documentation that makes it easy to learn and troubleshoot. Memphis is highly reliable and can deliver messages with low latency, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing.
One of the biggest strengths of Memphis is its ease of use. It comes with a simple and intuitive API that makes it easy to get started with. It also has an excellent documentation that makes it easy to learn and troubleshoot. Memphis is highly reliable and can deliver messages with low latency, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing.
When compared to RabbitMQ and Kafka, Memphis is faster and can deliver messages with lower latency. It is also easier to use and has a lower learning curve than both RabbitMQ and Kafka. Memphis also supports a wide range of protocols, including HTTP, MQTT, and AMQP, which makes it highly versatile.
Comparison with RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a popular message broker that is widely used in enterprise environments. It is built on top of the Erlang programming language and is designed to be highly reliable and scalable. RabbitMQ is known for its advanced features, such as message routing, clustering, and federation.
When compared to Memphis, RabbitMQ is more complex and has a steeper learning curve. It is also slower than Memphis and has higher latency when delivering messages. RabbitMQ has more advanced features than Memphis, but these features come at the cost of increased complexity.
Comparison with Kafka
Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that is widely used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. It is built on top of the Java programming language and is designed to be highly scalable and fault-tolerant. Kafka is known for its high throughput and low latency, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing.
When compared to Memphis, Kafka is more complex and has a steeper learning curve. It is also slower than Memphis and has higher latency when delivering messages. Kafka has more advanced features than Memphis, such as the ability to store and process streams of data over extended periods of time, but these features come at the cost of increased complexity.
Example of using Memphis
How to use Memphis, let's look at an example with code. Suppose i have two applications that need to communicate asynchronously. The first application produces messages, while the second application consumes messages. To use Memphis for this, i first need to set up a Memphis broker and create a queue for the messages. Here's how to do it.
const { memphis } = require('memphis');
const broker = new memphis.Broker();
const queue = broker.createQueue('example_queue');
const producer = broker.createProducer('example_queue');
producer.send({ message: 'Hello, World!' });
const consumer = broker.createConsumer('example_queue');
consumer.on('message', (msg) => {
console.log(`Received message: ${msg.content.toString()}`);
});
This code creates a Memphis broker, creates a queue called 'example_queue', and sets up a producer and consumer for the queue. The producer sends a message to the queue, while the consumer listens for messages and prints them to the console. This is just a simple example, but it demonstrates how easy it is to use Memphis for asynchronous communication between applications.
Another example of how to use Memphis to send message from a producer to a consumer.
use memphis::client::MemphisClient;
let client = MemphisClient::new("localhost:5555").unwrap();
let message = "Hello, world!";
let topic = "my-topic";
client.send(topic, message).unwrap();
This example creates a Memphis client and sends a message to the "my-topic" topic.
Limitations of Memphis
While Memphis is an excellent messaging system, there are still some limitations that exist.
One of the main limitations is its lack of support for some messaging patterns such as publish-subscribe and topic-based messaging. This can make it difficult to implement certain types of applications that require these patterns.
Another limitation is its lack of support for dynamic routing, which can make it challenging to route messages to specific destinations dynamically. Memphis also has a smaller community.
Conclusion
Memphis is a reliable and high-performance messaging system that is easy to use and has several strengths when compared to other similar messaging systems such as RabbitMQ and Kafka. Although it does have some limitations, they are constantly working to improve Memphis and make it more versatile and robust.
It is still a beta version and has many limitations, but I think it has many strengths and features a new technology stack that is easy to use. If you try it once, I recommend you to try it because you will be able to apply it quickly when the official version is relesed someday.


 One of the biggest strengths of Memphis is its ease of use. It comes with a simple and intuitive API that makes it easy to get started with. It also has an excellent documentation that makes it easy to learn and troubleshoot. Memphis is highly reliable and can deliver messages with low latency, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing.
One of the biggest strengths of Memphis is its ease of use. It comes with a simple and intuitive API that makes it easy to get started with. It also has an excellent documentation that makes it easy to learn and troubleshoot. Memphis is highly reliable and can deliver messages with low latency, making it ideal for use cases that require real-time data processing.